The Key to Email Security and Deliverability
Cybercriminals can easily send emails that look like they’re coming from your company — a tactic called email spoofing. DMARC is an essential protocol for protecting your email domain from spoofing and phishing attacks.
What Is DMARC in Email?
Fake emails are frequently used in phishing scams to deceive your customers into sharing sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers. Every time this occurs, it damages their trust in your brand. Beyond that, spoofing and phishing attempts can lower the chances that your genuine emails will make it to customers’ inboxes at all.
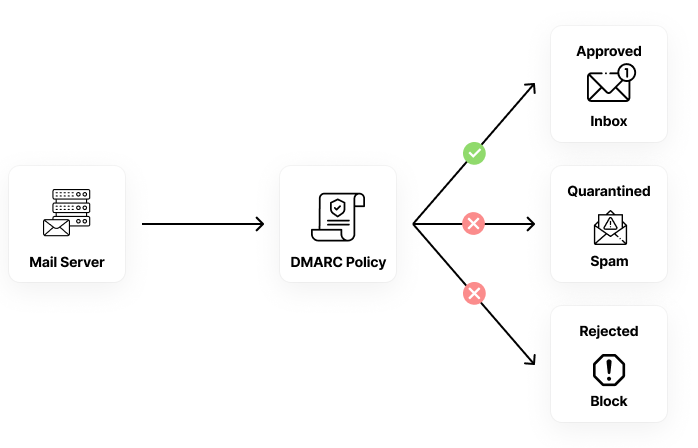
DMARC enables you to instruct email providers to either reject or quarantine messages that don’t originate from approved sources. Approval is determined using SPF and DKIM, two common authentication methods that verify an email’s legitimacy.
So, how can you defend your brand and communications from these threats?
By using DMARC (Domain-Based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) — a protocol designed to block unauthorized use of your domain in outgoing emails.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
What it does: Enables you to designate which servers are allowed to send emails from your domain.
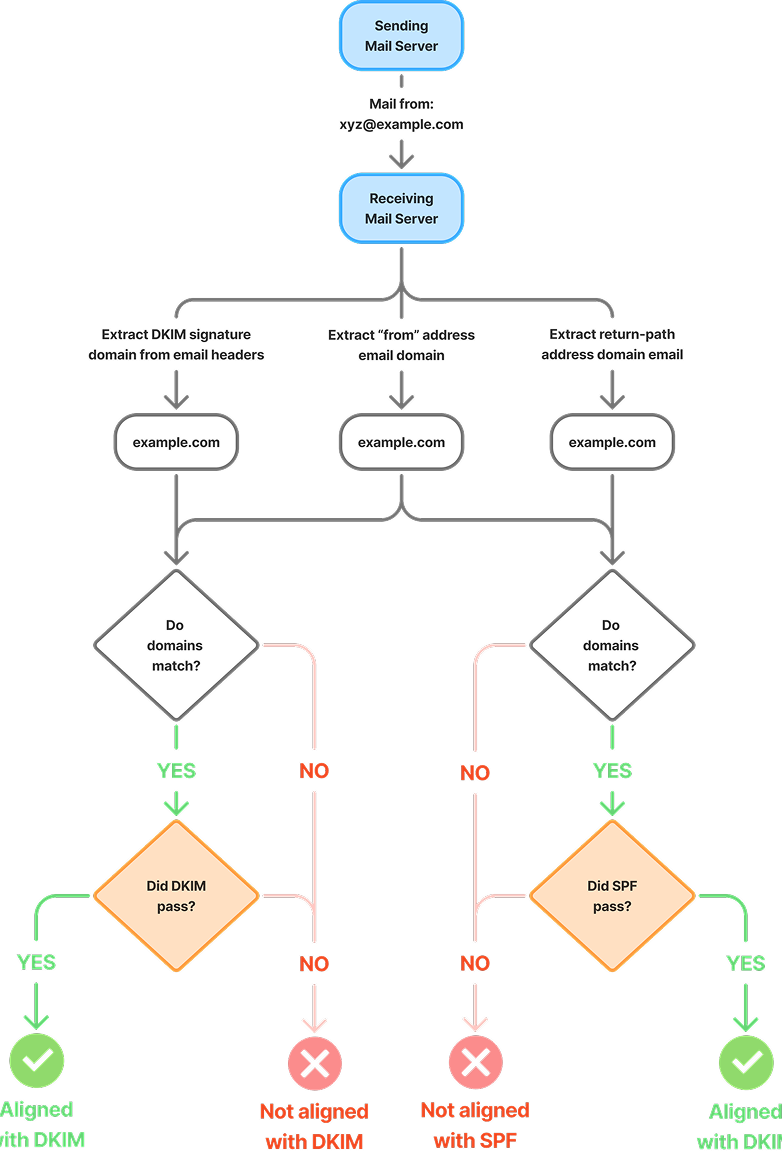
How it works: You publish a list of trusted servers in your domain’s DNS. If an email comes from somewhere else, it can be blocked or marked as suspicious.
Why it matters: Helps stop attackers from sending fake emails using your domain name.
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
What it does: Adds a digital signature to your emails so the receiver can check if the email really came from your domain.
How it works: Your mail server signs the email with a private key, and the receiver checks the signature using a public key stored in your DNS.
Why it matters: Makes sure your email content is authentic.
DMARC
What it does: Combines SPF and DKIM results and tells the receiver what to do if an email fails the checks.
You can configure your DMARC policy to instruct receivers to do three things:
- Nothing – Just collect reports, but don’t block anything.
- Quarantine – Send suspicious emails to spam.
-
Reject – Block emails that fail the checks.
How Does DMARC Work with SPF and DKIM?
Once DMARC is configured for your domains, providers like Yahoo and Gmail begin sending daily reports showing how emails sent from your domain perform in terms of DMARC compliance. DMARCeye collects and interprets these reports for you, displaying the insights through an easy-to-use dashboard so you can monitor the sources and legitimacy of your email traffic, and take action if needed.